Archives
Anti apoptotic Bcl proteins have become
Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins have become attractive targets for anti-cancer agents development, because they are associated with progression of a wide variety of human cancers., , The small-molecular Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax (ABT-199) () has been approved recently for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who have a chromosomal abnormality called 17p deletion., At present, ABT-199 is under clinical trials for the treatment of MM. HDACs, which are frequently dysregulated in cancer, can be subdivided into 4 classes: classes I, II and IV (zinc dependent enzymes), and class III (nicotinamide mi2 dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent). Five HDAC inhibitors vorinostat (SAHA), romidpesin, belinostat, chidamide, and panobinostat have been approved as anti-cancer agents., The class IIb HDAC, HDAC6 is distinguished by its ability to deacetylate α-tubulin and HSP90, in addition to the modification of histone., A selective HDAC6 inhibitor ACY-1215 () is currently under clinical trials for the treatment of MM.
Most recommended treatment protocols for the patients with relapsed refractory MM comprise a combination of drugs with different mechanisms of action, such as lenalidomide or bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone, or even triplet regimens., HDAC inhibitors and Bcl-2 inhibitors were in combination with above approved chemotherapeutic agents in clinic or clinical trials for the treatment of MM, and showed synergistic effects with them., , , Additionally, Bcl-2 inhibitors and HDAC inhibitors were discovered to have synergistic interactions in MM cell lines, at least in part, through Bim upregulation., The combination of Bcl-2 inhibitors and HDAC inhibitors were further proved to overcome adaptive bortezomib resistance . Above research provide the reasonability of the therapeutic strategies combining these two type of agents for the treatment of MM.
Considered the more predictable pharmacokinetic profile, less drug-drug interactions, the improved convenience, the potential superior efficacy and lower toxicity, drugs with optimal multi-target activities may represent a valuable complement or even alternative to therapeutic regimens based on drug combinations., In this study, a series of Bcl-2/HDAC dual-target inhibitors w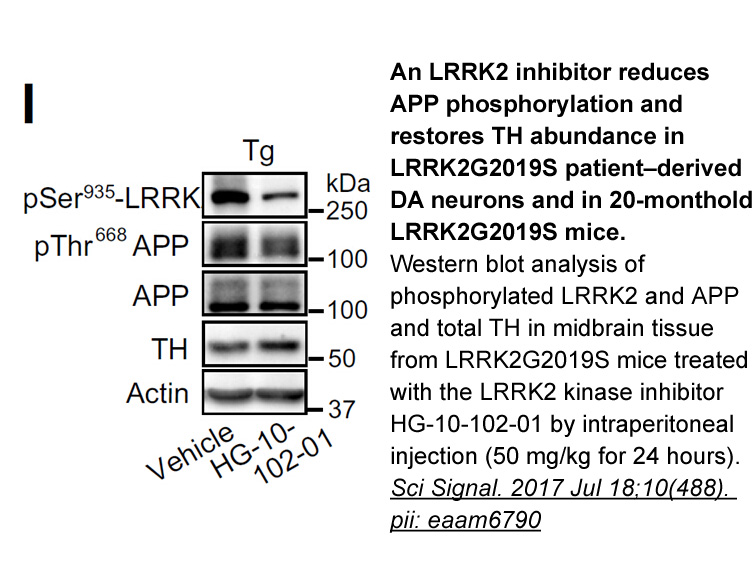 ere designed. It is well known that the HDAC inhibitors have a general structure consisting of a cap region, a zinc-binding group (ZBG), and a linker region which connects the two (). Hydroxamic acid group is the most common used ZBG. It chelates the zinc ion in the active site and is critical for the inhibitory activity. However, the cap region, the so-called surface recognition domain, occludes the entrance of the active site pocket. It is predominantly responsible for selectivity and tolerates a large change., In addition, the docking binding mode of ABT-199 and Bcl-2 protein () was obtained using the complex crystal structure of its analog as template (PDB ID: ). Based on the three-dimensional pharmacophore we constructed before,, , the groups binding in the P1, L and P2 pockets of binding groove played major roles in the interaction with Bcl-2 protein. While the tetrahydropyranyl methyl group binding in the P3 pocket exposed to the solvent and had less effect on the binding. As a result, Bcl-2/HDAC dual-target inhibitors were designed by the replacement of the tetrahydropyranyl methyl group of ABT-199 by hydroxamic acid group with different linkers ().
The synthetic routes of title compounds were shown in . Intermediate was obtained by electrophilic substitution reaction of 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene under the condition of chlorosulfonic acid, and then intermediate was obtained under the condition of aqueous ammonia in ice bath. Using different amino acid as start material, esterification reaction was carried out under the condition of thionyl chloride and ethanol to produce the intermediates –. Intermediates – was yielded from intermediates and intermediates – by nucleophilic substitution reaction under the condition of DIEA in DMSO. Compound was synthesized by the method reported. Then intermediates – and were treated with condensation agent EDCI to obtain intermediate –. It was ammoniated in methanol solution of hydroxylamine hydrochloride in which KOH had been dissociated, title compounds was obtained finally.
ere designed. It is well known that the HDAC inhibitors have a general structure consisting of a cap region, a zinc-binding group (ZBG), and a linker region which connects the two (). Hydroxamic acid group is the most common used ZBG. It chelates the zinc ion in the active site and is critical for the inhibitory activity. However, the cap region, the so-called surface recognition domain, occludes the entrance of the active site pocket. It is predominantly responsible for selectivity and tolerates a large change., In addition, the docking binding mode of ABT-199 and Bcl-2 protein () was obtained using the complex crystal structure of its analog as template (PDB ID: ). Based on the three-dimensional pharmacophore we constructed before,, , the groups binding in the P1, L and P2 pockets of binding groove played major roles in the interaction with Bcl-2 protein. While the tetrahydropyranyl methyl group binding in the P3 pocket exposed to the solvent and had less effect on the binding. As a result, Bcl-2/HDAC dual-target inhibitors were designed by the replacement of the tetrahydropyranyl methyl group of ABT-199 by hydroxamic acid group with different linkers ().
The synthetic routes of title compounds were shown in . Intermediate was obtained by electrophilic substitution reaction of 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene under the condition of chlorosulfonic acid, and then intermediate was obtained under the condition of aqueous ammonia in ice bath. Using different amino acid as start material, esterification reaction was carried out under the condition of thionyl chloride and ethanol to produce the intermediates –. Intermediates – was yielded from intermediates and intermediates – by nucleophilic substitution reaction under the condition of DIEA in DMSO. Compound was synthesized by the method reported. Then intermediates – and were treated with condensation agent EDCI to obtain intermediate –. It was ammoniated in methanol solution of hydroxylamine hydrochloride in which KOH had been dissociated, title compounds was obtained finally.